pv magazine test: October 2024 Results
By George Touloupas
This article was originally published in pv magazine – December 2024 edition. Learn more about the pv magazine test here.
George Touloupas, senior director of technology and quality at Clean Energy Associates, analyzes the October 2024 results from the pv magazine Test outdoor installation in Xi’an, China.
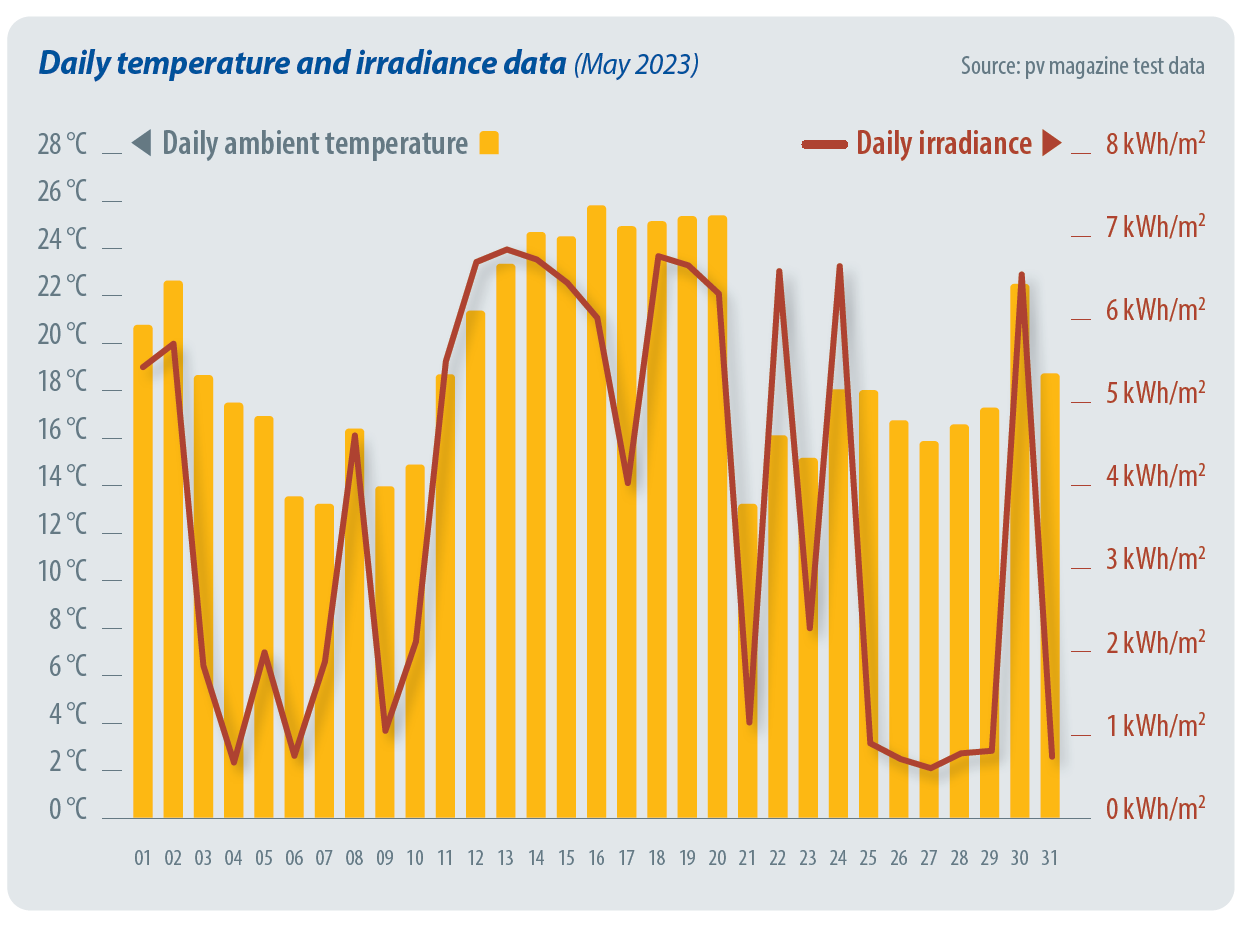
During the month of October, system downtime has meant that two days of data have been excluded. The first chart below shows the meteo station data (irradiance and ambient temperature) for October 2024.
Figure 1: Daily temperature and irradiance data - October 2024
Over this period, the average bifacial boost was 7.60%. Bifacial boost is defined as the relative advantage of the average specific energy yield of all bifacial products compared to the average specific energy yield of all monofacial passivated emitter rear contact (PERC) products.
As only one heterojunction (HJT) sample has been installed, its performance is not representative of HJT technology. We will therefore stop reporting the relative yield for HJT in October 2024 and resume when we have more heterojunction samples installed.
Table 1: Bifacial boost - July 2024 to October 2024
Table 2: Specific energy yield ranking of negatively doped, n-type bifacial tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) and HJT modules - October 2024
Table 3: Specific energy-yield ranking of bifacial PERC modules - October 2024
Table 4: Specific energy-yield ranking of monofacial modules - October 2024
Notes on the energy yield measurements:
The energy yield comparison among various technologies, including bifacial boost, analyzes products installed since the beginning of 2019.
The energy yield is given in Wh/Wp and is calculated by dividing the energy produced by the module by the Pmax at STC of the module. This Pmax is the maximum STC power after a process of stabilization.
The results are grouped in categories, per solar module type.
The bifacial boost depends on a number of parameters: the bifaciality factor, the installation geometry, the albedo of the ground, and the sun angle and diffuse irradiance. The ground in this case is gray gravel.
Figure 2: Specific energy yield of n-type bifacial (TOPCon and HJT), bifacial PERC, and monofacial modules - October 2024
Figure 3: Relative yield of different technologies - October 2024
Test cooperation
pv magazine test is a cooperative effort involving pv magazine, CEA, Gsolar and Hoymiles. All testing procedures are carried out at Gsolar’s test laboratory in Xi’an, China. CEA supervises these tests and designed both the indoor and outdoor testing procedures.