pv magazine Test 2.0
By George Touloupas and Huatian Xu
This article was originally published in pv magazine – March 2025 edition.
After more than seven years, pv magazine test is entering a new phase. Significant changes are on the horizon as we update and overhaul the program. George Touloupas, Vice President, ESG and New Services at Clean Energy Associates (CEA), and Huatian Xu, Director of Technology and Quality at CEA, introduce the new “pv magazine test 2.0” setup to assess PV modules in the lab and outdoors.
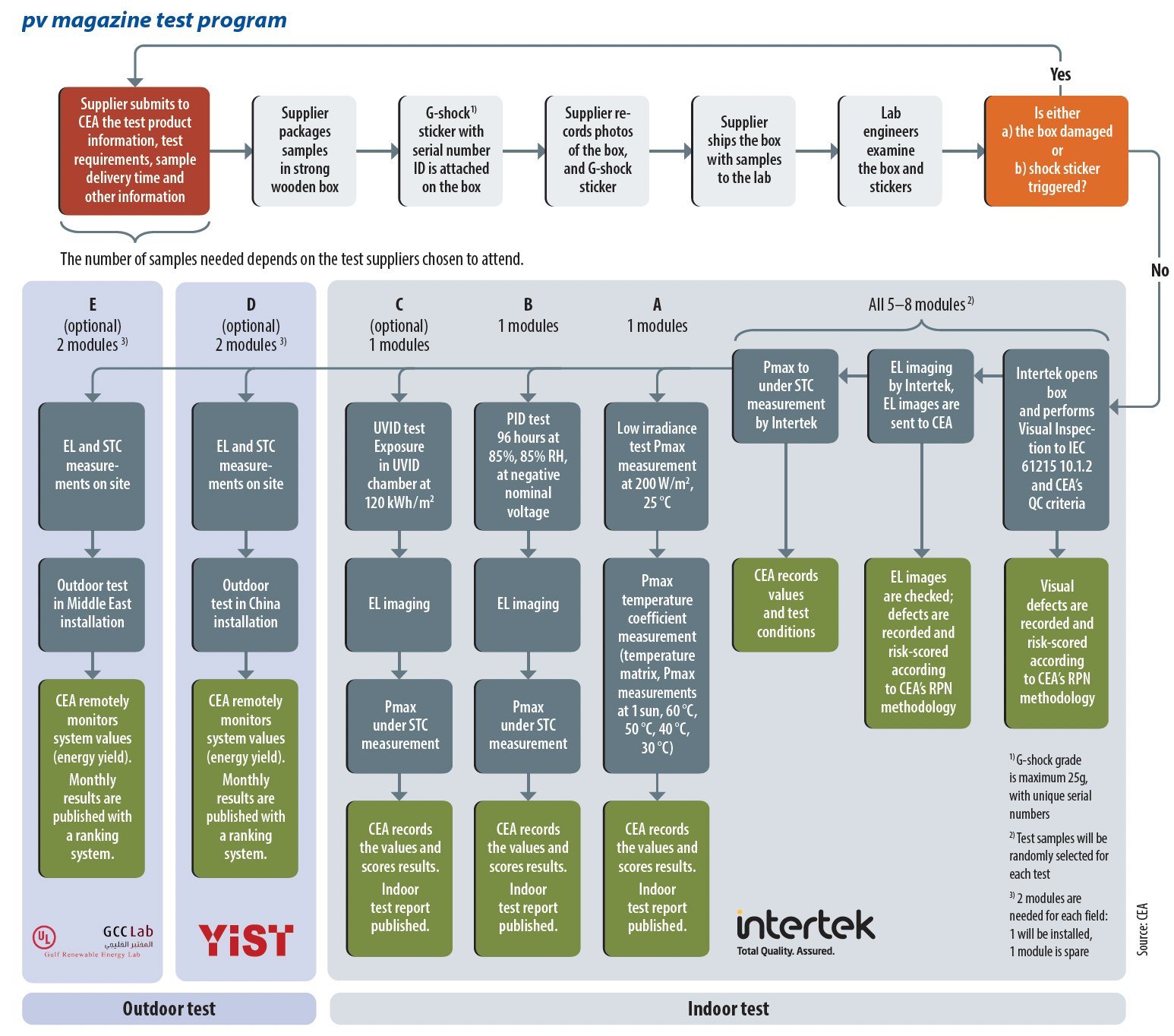
pv magazine test began in 2017. Since then, Chinese PV testing equipment supplier Gsolar has provided support as a program partner, hosting the outdoor rooftop installation where the long-term performance of modules is monitored, and putting modules through their paces in lab-based quality and performance tests, all at its facility in Xi’an, China.
We have reached a bottleneck in terms of Xi’an resources. Rooftop space is running out and the equipment required to fully test and characterize emerging PV technology demands more investment than was budgeted for at Gsolar’s lab, so three new partners have been invited to bring their resources to pv magazine test 2.0.
Intertek’s Involvement
CEA parent Intertek provides industrial quality-assurance testing, inspection, and certification services. It has supported manufacturers in Japan and the United States with certification.
CEA will continue to lead the daily management of the testing program and Intertek China will handle in-house lab tests, including the measurement of the initial power of samples before outdoor field monitoring. Intertek has comprehensive lab-testing capabilities covering most testing items in the PV industry. Formal testing reports, endorsed by Intertek, will be released for each sample tested.
Rear-facing sensors at the Yinchuan test site allow technicians to monitor solar radiation on the rear side of bifacial modules.
YIST Partnership
pv magazine test program
The Yangtze Institute for Solar Technology (YIST) is a photovoltaics innovation center founded in 2021 by the Jiangsu Industrial Technology Research Institute and the Jiangyin municipal government. It is supported by several major PV manufacturers. Led by PV expert and Sun Yatsen University Prof. Shen Hui, YIST has attracted solar talent including scientist Pierre Verlinden, US National Renewable Energy Laboratory Senior Scientist Wang Qi, and Feng Zhiqiang, deputy director of the China National Key Laboratory of Photovoltaic Science and Technology.
YIST has published six papers, including one in Science, with 18 authorized patents and 39 patent applications, achieving 16 domestic inventions.
One of YIST’s research programs involves monitoring the real-time performance of PV modules under different environmental conditions at various outdoor solar power plants. Moving forward, YIST will support the pv magazine test program by sharing its testing field in Yinchuan, Ningxia. That testing field is operated by the China National Center of Supervision and Inspection on Solar PV Products Quality (CPVT) and YIST has rented space there to conduct research on the real-time performance of PV modules in operation.
The Yinchuan testing field represents a typical PV application location in China. The region benefits from an annual radiation intensity of more than 500 W/ m. for more than 2,300 hours, with average daily direct irradiation amounting to 5.68 kWh/m2.
Covering 290,000 m. of outdoor testing area, the facility also boasts an impressive 6,000 m. indoor laboratory capable of supporting high-accuracy module power tests. The site includes various specialized facilities such as an outdoor PV testing site, an indoor laboratory, a mobile inspection platform for PV plants, and an energy storage testing platform.
The complex comprises 15 main functional areas, including a PV-sample degradation area, an energy storage product testing area, and a multi- scenario distributed- system testing area. Customized outdoor empirical tests can be conducted on PV modules, materials, components, cleaning robots, PV and energy storage systems, and other PV-related products. This makes the Yinchuan facility one of the largest third-party PV outdoor, empirical testing platforms in China.
The new outdoor test field at YIST will employ a similar setup to that in Xi’an, with some upgraded devices. With support from power electronics manufacturer and pv magazine test partner Hoymiles, a new microinverter type, the HMS-2000D, has been integrated into our new program. This device is an upgraded version of the HMS-2000 model previously in use at the Xi’an facility. It retains all the features of its predecessor, such as:
High power output of up to 2 kVA, with support for very high direct-current input to accommodate the largest, most highly powered modules.
Two independent maximum power point trackers (MPPTs) for up to four terminals for module connection, optimizing module performance with up to 99.8% MPPT efficiency to ensure high performance at a reasonable cost.
A sub-1GHz wireless solution, ensuring stable communication with the Hoymiles gateway data transfer unit, providing uninterrupted and stable communication. This feature is particularly valuable in commercial and industrial settings and contributes to overall system reliability.
IP67 protection, which has proven effective in our application at the Xi’an field.
Currently, we will connect no more than two samples to each microinverter (one to each MPPT) to ensure the independent performance of each sample. Thanks to its circuit design, the HMS-2000D doesn’t require any additional adaptor for such connections, further reducing deviation among different module types.
With YIST’s investment in the field monitoring system, our data analysis capabilities have significantly improved in the new test setup. We now have better tools to review data across different samples and the system has the intelligence to flag suspicious data errors during operation and automatically remove or correct them, pending our review and approval. Previously, this work was conducted manually and required considerable effort.
Another improvement is in meteorological data collection. In the new field, we can collect ultraviolet (UV) irradiance as well as module rear side performance data separately, in addition to common irradiance data. This will enable us to analyze potential UV degradation effects, which are widely known in the industry. In addition to these functional improvements, we expect a more stable electric grid at the new field, resulting in less downtime.
The operation of pv magazine test 2.0 at the Yinchuan field commenced in the first week of December 2024. To start at an appropriate scale, spare samples of several products that began outdoor operation in Xi’an in 2024, or late 2023, were installed in Yinchuan as part of the first batch. Other new samples from manufacturers are in the process of preparation and testing. We anticipate a rapid increase in sample scale at the Yinchuan facility soon.
Modules for the pv magazine test partnership with YIST will be installed at the China National Center of Supervision and Inspection on Solar PV Products (CPVT) site in Yinchuan, Ningxia.
Gulf Renewable Laboratories
In addition to Yinchuan, we are planning new outdoor testing fields in other regions. Our next target is the Middle East, where pv magazine has signed a cooperation agreement with Gulf Renewable Laboratories, a subsidiary of GCC Electrical Testing Laboratory (see box to the left). This extends the pv magazine test program to a second outdoor testing facility, in Dammam, Saudi Arabia. More details on this extension will follow in the coming months.
Adding a Gulf Test
pv magazine test’s new partner is Gulf Renewable Energy Lab (GRL), based in Dammam, Saudi Arabia. GRL offers a wide range of testing, inspection and certification (TIC) services, as well as consulting services in the field of renewable energy. The innovation center is a joint venture between GCC Electrical Testing Laboratory (GCC Lab) and US-based TIC provider Underwriters Laboratories. GCC Lab was formally established in 2016 by 10 strategic Saudi Arabian and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) stakeholders. The GCC Lab complex was inaugurated in January 2023 in Dammam’s third industrial city. GCC Lab occupies 170,000 mÇ of land and includes eight advanced testing and research centers in the fields of conventional and renewable energy, safety, quality, and inspection services.
GRL is one of the eight centers and a key part of its mission is to serve as a localization enabler in the Saudi Arabia and GCC region, and to support the local knowledge economy. Its portfolio of TIC services includes more than 60 standard tests and GRL has developed standards that go beyond industry stipulations to address the severe weather conditions in the GCC and Middle East and North Africa region. With its high humidity, heat, UV, and dust levels, the GRL outdoor test facility in Dammam, in eastern Saudi Arabia, is ideally suited to test the performance and durability of PV modules in the harsh desert environment.
In January 2025, pv magazine met with the GRL team in Dammam to discuss the pv magazine test cooperation and the installation of the first set of modules in the first half of this year. It was evident that GRL is one of the largest and most sophisticated renewable energy labs in the world, with state-of-the-art indoor testing facilities and an outdoor testing area that was recently expanded from 1,000 mÇ to 3,000 mÇ. As modules are installed in Dammam, GRL will begin monitoring their performance and after one full month of data has been collected, CEA will include this data in the monthly report published in pv magazine’s global edition. This way, readers of pv magazine will not only receive test data from the pv magazine test field in China but also from GRL’s facility in Dammam, where modules will face even tougher weather conditions that will test the reliability, durability, and efficiency of the latest generation of module products.